Finding Angles
SAT Subject Test in Math II · Learn by Concept
Help Questions
SAT Subject Test in Math II › Finding Angles

The above hexagon is regular. What is 
None of the other responses is correct.
Explanation
Two of the angles of the quadrilateral formed are angles of a regular hexagon, so each measures

The four angles of the quadrilateral are 


If the angles 


Explanation
Supplementary angles sum up to 180 degrees.
Add five on both sides.
Divide by negative five on both sides to determine 
The answer is:
If a set of angles are supplementary, what must be the other angle if a given angle is 
Explanation
Supplementary angles must add up to 180 degrees.
To find the missing angle, subtract the known angle from 180 degrees.
The answer is:
What angle do the minute and hour hands of a clock form at 6:15?
Explanation
There are twelve numbers on a clock; from one to the next, a hand rotates 



Suppose a set of intersecting lines. If an angle is 120 degrees, what must be the sum of the adjacent angle and the vertical angle to the given angle?
Explanation
In an intersecting pair of lines, recall that vertical angles will always equal.
The adjacent angle with the given angle will form a straight line, and both of the angles must sum to 180 degrees.
Subtract 120 from 180 to get the adjacent angle.
Sum the two angles.
The answer is:
In triangle 






None of the other responses is correct.
Explanation
Since the measures of the three interior angles of a triangle must total 
All three angles have measure less than 


In 








None of the other responses is correct.
Explanation



Since the measures of the three interior angles of a triangle must total 








If two angles of a triangle are 
Explanation
Every pi radians equal 180 degrees.
We can choose to convert the radians to degrees first.
The sum of these two angles are:
Subtract this value from 
The answer is:

The above figure is a regular decagon. Evaluate 
Explanation
As an interior angle of a regular decagon, 
![m \angle B = \left [\frac{180(10-2)}{10} \right ] ^{\circ }= 144^{\circ }](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/217578/gif.latex)
Since 

The sum of the measures of a triangle is 








































 and
and  .
.



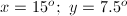
 all reside along one line, therefore, their sum must be
all reside along one line, therefore, their sum must be 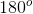 .
.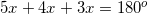


 and
and 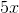 are opposite angles, they must be equal.
are opposite angles, they must be equal.






























