Organic Concepts - Organic Chemistry
Card 1 of 1120
Which of the following is the worst nucleophile?
Which of the following is the worst nucleophile?
Tap to reveal answer
 is least nucleophilic because its oxygen has no negative charge, and oxygen is more electronegative than sulfur, thus the lone pair of electrons on oxygen are more stable than they would be on sulfur or nitrogen.
is least nucleophilic because its oxygen has no negative charge, and oxygen is more electronegative than sulfur, thus the lone pair of electrons on oxygen are more stable than they would be on sulfur or nitrogen.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following sets of nucleophiles are correctly listed from strongest to weakest in a protic solvent?
Which of the following sets of nucleophiles are correctly listed from strongest to weakest in a protic solvent?
Tap to reveal answer
In a protic solvent, the larger the atom the better the nucleophile. Atomic radius increases as you go down a group on the periodic table. Also, the more electronegative an atom/nucleophile, like fluorine, the higher the capability of forming hydrogen bonds with protic solvents, thus hindering their effectiveness as a nucleophile.
In a protic solvent, the larger the atom the better the nucleophile. Atomic radius increases as you go down a group on the periodic table. Also, the more electronegative an atom/nucleophile, like fluorine, the higher the capability of forming hydrogen bonds with protic solvents, thus hindering their effectiveness as a nucleophile.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is the best nucleophile?
Which of the following is the best nucleophile?
Tap to reveal answer
The ordering from best nucleophile to worst nucleophile is as follows:

Smaller molecules are better nucleophiles than larger ones (they are not as sterically hindered).  is a better nucleophile than
is a better nucleophile than  because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen (Look for the the lower electronegativity on the atom holding the lone pair of electrons). Thus, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen are not as stable as those on oxygen, and will readily donate its pair of electrons to another species.
because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen (Look for the the lower electronegativity on the atom holding the lone pair of electrons). Thus, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen are not as stable as those on oxygen, and will readily donate its pair of electrons to another species.
The ordering from best nucleophile to worst nucleophile is as follows:
Smaller molecules are better nucleophiles than larger ones (they are not as sterically hindered). 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
I. The best nucleophiles are negatively charged
II. Smaller molecules are better nucleophiles than larger ones
III. The smaller the atom, the better the nucleophile (protic solvent)
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
I. The best nucleophiles are negatively charged
II. Smaller molecules are better nucleophiles than larger ones
III. The smaller the atom, the better the nucleophile (protic solvent)
Tap to reveal answer
The larger the atom, not molecule, the better the better the nucleophile  . Atomic radius increases as you go down a group on the periodic table. Nucleophilicity can also be determined according to strength of the anion as a conjugate base. Remember that
. Atomic radius increases as you go down a group on the periodic table. Nucleophilicity can also be determined according to strength of the anion as a conjugate base. Remember that  is the strongest acid and thus has the weakest/least stable conjugate base.
is the strongest acid and thus has the weakest/least stable conjugate base.
The larger the atom, not molecule, the better the better the nucleophile 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is the best leaving group?
Which of the following is the best leaving group?
Tap to reveal answer
 is the weakest base as its negative charge is spread out more evenly over the large atom. Thus, it is the best leaving group of these four halogens. It is the best leaving group due to its largest size and distribution of negative charge.
is the weakest base as its negative charge is spread out more evenly over the large atom. Thus, it is the best leaving group of these four halogens. It is the best leaving group due to its largest size and distribution of negative charge.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following compounds can be considered a Lewis base?
Which of the following compounds can be considered a Lewis base?
Tap to reveal answer
A Lewis base is a compound that donates a pair of electrons. The only compound shown that possesses an electron pair that can be donated is ammonia.  is the Lewis base.
is the Lewis base.  and
and  are Lewis acids and are therefore wrong. Neither carbon dioxide nor methane are Lewis bases.
are Lewis acids and are therefore wrong. Neither carbon dioxide nor methane are Lewis bases.
A Lewis base is a compound that donates a pair of electrons. The only compound shown that possesses an electron pair that can be donated is ammonia. 


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is least likely to result in substitution when added to a secondary halide.
Which of the following is least likely to result in substitution when added to a secondary halide.
Tap to reveal answer
To promote elimination rather than substitution, a molecule must be a strong base and weakly nucleophilic. Typically weak nucleophiles are large and bulky, which therefore have difficulty undergoing backside attack. Only tert-butoxide is a weak nucleophile, due to its branching, meaning it is least likely to participate in substitution.
To promote elimination rather than substitution, a molecule must be a strong base and weakly nucleophilic. Typically weak nucleophiles are large and bulky, which therefore have difficulty undergoing backside attack. Only tert-butoxide is a weak nucleophile, due to its branching, meaning it is least likely to participate in substitution.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of these qualities applies to a good nucleophile?
Which of these qualities applies to a good nucleophile?
Tap to reveal answer
A good nucleophile should not be bulky. If the nucleophile is bulky, the compound will not be able to reach the carbonyl carbon, where the reaction occurs. With increased steric hindrance due to a bulkier nucleophile, the reaction will run slowly, and the compound is not a good nucleophile. Good nucleophiles also want to give away electrons so that the reaction can occur. This means that conjugate bases make better nucleophiles than acids.
A good nucleophile should not be bulky. If the nucleophile is bulky, the compound will not be able to reach the carbonyl carbon, where the reaction occurs. With increased steric hindrance due to a bulkier nucleophile, the reaction will run slowly, and the compound is not a good nucleophile. Good nucleophiles also want to give away electrons so that the reaction can occur. This means that conjugate bases make better nucleophiles than acids.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

For which of the following acid-base reactions will the equilibrium lie on the left side?
For which of the following acid-base reactions will the equilibrium lie on the left side?
Tap to reveal answer
The pKa value indicates how strong an acid is, and acid strength increases as pKa decreases. The side of a reaction with a lower pKa is going to dissociate more, pushing the equilibrium over to the other side. The equilibrium will thus lie on the side with the HIGHER pKa.

Since the pKa of acetic acid (4.76) is higher than the pKa of trifluoroacetic acid (0), the reaction will shift to the left to reach equilibrium.
The pKa value indicates how strong an acid is, and acid strength increases as pKa decreases. The side of a reaction with a lower pKa is going to dissociate more, pushing the equilibrium over to the other side. The equilibrium will thus lie on the side with the HIGHER pKa.
Since the pKa of acetic acid (4.76) is higher than the pKa of trifluoroacetic acid (0), the reaction will shift to the left to reach equilibrium.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Electron donation and withdrawal have important impacts on acidity. What R group would yield the species with the highest pKa?

Electron donation and withdrawal have important impacts on acidity. What R group would yield the species with the highest pKa?

Tap to reveal answer
This question tests your knowledge about electron donation, as well as acidity. The question asks you to identify the species with the highest pKa, which means you need to look for the R group that will be the most donating. Electron donation will destabilize the conjugate base anion, localized partially on the oxygen of the hydroxyl moiety; the result is a less acidic acid, and a higher pKa.
Of the answer choices, three are electron-withdrawing. These include the nitro (-NO2), the ketone (-CCOMe), and the carboxyl (-COOH). The only answer choices that are electron-donating are the methyl (-Me), and the ether (-OMe). As the ether can push its lone pairs into the pi system of the ring and the carboxyl group, it is the stronger electron-donating group. The methyl can only donate electrons through inductive effects, or electronic polarization of sigma bonds, which is not as strong of an electron donation effect. Thus, -OMe is the correct answer.
This question tests your knowledge about electron donation, as well as acidity. The question asks you to identify the species with the highest pKa, which means you need to look for the R group that will be the most donating. Electron donation will destabilize the conjugate base anion, localized partially on the oxygen of the hydroxyl moiety; the result is a less acidic acid, and a higher pKa.
Of the answer choices, three are electron-withdrawing. These include the nitro (-NO2), the ketone (-CCOMe), and the carboxyl (-COOH). The only answer choices that are electron-donating are the methyl (-Me), and the ether (-OMe). As the ether can push its lone pairs into the pi system of the ring and the carboxyl group, it is the stronger electron-donating group. The methyl can only donate electrons through inductive effects, or electronic polarization of sigma bonds, which is not as strong of an electron donation effect. Thus, -OMe is the correct answer.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the given compounds is not a Lewis acid?
Which of the given compounds is not a Lewis acid?
Tap to reveal answer
A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor.
The carbocation is clearly trying to accept electrons due to the positive charge.  is ionic and neutral. The boron in
is ionic and neutral. The boron in  has only three electrons, and they are all creating bonds with fluorines.
has only three electrons, and they are all creating bonds with fluorines.
The correct answer has a lone pair on the nitrogen, and thus has electrons to donate and as a Lewis base.  is not a Lewis acid.
is not a Lewis acid.
A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor.
The carbocation is clearly trying to accept electrons due to the positive charge. 

The correct answer has a lone pair on the nitrogen, and thus has electrons to donate and as a Lewis base. 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following R groups would increase the rate of the following substitution reaction?
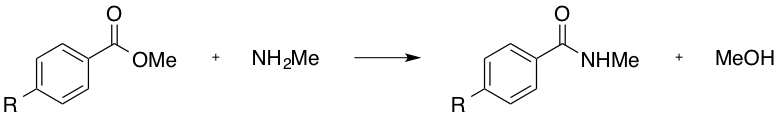
Which of the following R groups would increase the rate of the following substitution reaction?

Tap to reveal answer
The above reaction would more readily proceed if the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon were enhanced. This may be achieved through electron withdrawal via the R group.
The ether (-OMe), the methyl (-Me), and the hydroxyl (-OH), would all produce a electron-donating effect, and are thus incorrect answers.
The nitro group (-NO2), and the positively charged, tetra-substituted amino group (consider the structure once this trimethyl amino group is connected to the aryl ring) are both electron-withdrawing. As the trimethyl amino group will have an overall positive charge (and the nitro group is neutral overall), the trimethyl amino group is the stronger electron-withdrawing moiety, and is thus the correct answer.
The above reaction would more readily proceed if the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon were enhanced. This may be achieved through electron withdrawal via the R group.
The ether (-OMe), the methyl (-Me), and the hydroxyl (-OH), would all produce a electron-donating effect, and are thus incorrect answers.
The nitro group (-NO2), and the positively charged, tetra-substituted amino group (consider the structure once this trimethyl amino group is connected to the aryl ring) are both electron-withdrawing. As the trimethyl amino group will have an overall positive charge (and the nitro group is neutral overall), the trimethyl amino group is the stronger electron-withdrawing moiety, and is thus the correct answer.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The molecule pictured is known as rapamycin, or Sirolimus, and is used as an immunosuppressant during organ transplants. Which of the following colored carbonyl groups is the most electrophilic?

The molecule pictured is known as rapamycin, or Sirolimus, and is used as an immunosuppressant during organ transplants. Which of the following colored carbonyl groups is the most electrophilic?

Tap to reveal answer
Note that many of these carbonyl groups are actually part of various functional groups. For example, the gold is an aldehyde, the green and purple are both ketones, the red is an amide, and the blue is an ester. We know the electrophilicity of carbonyl-containing functional groups is as follows:

Thus, our aldehyde, in gold, is the most electrophilic.
Note that many of these carbonyl groups are actually part of various functional groups. For example, the gold is an aldehyde, the green and purple are both ketones, the red is an amide, and the blue is an ester. We know the electrophilicity of carbonyl-containing functional groups is as follows:

Thus, our aldehyde, in gold, is the most electrophilic.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which compound is not a Lewis acid?
Which compound is not a Lewis acid?
Tap to reveal answer
A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor.
 is an ionic molecule and is neutral.
is an ionic molecule and is neutral.  and
and  have positive charges and are electron pair acceptors, as they are more stable when they are neutral.
have positive charges and are electron pair acceptors, as they are more stable when they are neutral.
The correct answer,  , has a lone pair on the nitrogen atom that can be donated to form bonds with other atoms, so it is a Lewis base.
, has a lone pair on the nitrogen atom that can be donated to form bonds with other atoms, so it is a Lewis base.
A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor.



The correct answer, 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of these is a typical electrophile?
Which of these is a typical electrophile?
Tap to reveal answer
Electrophiles are substances that accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond, and nucleophiles are those that donate an electron pair to form a covalent bond. The chloride and iodide ions are both nucleophiles, as they each have a charge of  and would thus be willing to donate their extra electron. Ammonia (
and would thus be willing to donate their extra electron. Ammonia ( ) is also a nucleophile, as the nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons to donate. The methyl carbocation (carbon attached to three hydrogen atoms, with a positive charge) is an electrophile. The positive charge on the carbon makes it willing to accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond.
) is also a nucleophile, as the nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons to donate. The methyl carbocation (carbon attached to three hydrogen atoms, with a positive charge) is an electrophile. The positive charge on the carbon makes it willing to accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond.
Electrophiles are substances that accept an electron pair to form a covalent bond, and nucleophiles are those that donate an electron pair to form a covalent bond. The chloride and iodide ions are both nucleophiles, as they each have a charge of 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following compounds would be the best nucleophile?
Which of the following compounds would be the best nucleophile?
Tap to reveal answer
A nucleophile acts by donating a pair of electrons to another atom's nucleus. In general, a negatively charged compound is going to be a stronger nucleophile than a neutral compound. In addition, as one proceeds down a given column of the periodic table, the nucleophilicity increases because the electrons are not held as tightly to the nucleus (electronegativity decreases).
 is the best nucleophile, because it has a negative charge (more electron density), and its electrons are held less tightly than those of
is the best nucleophile, because it has a negative charge (more electron density), and its electrons are held less tightly than those of  because sulfur is less electronegative than oxygen.
because sulfur is less electronegative than oxygen.
A nucleophile acts by donating a pair of electrons to another atom's nucleus. In general, a negatively charged compound is going to be a stronger nucleophile than a neutral compound. In addition, as one proceeds down a given column of the periodic table, the nucleophilicity increases because the electrons are not held as tightly to the nucleus (electronegativity decreases).


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The given molecule is known as voacamine. Multi-cyclic molecules with a high nitrogen content such as this one are known as alkaloids, and tend to be highly toxic. A chemist is attempting to react a sample of voacamine with an electrophilic reagent known as Boc anhydride, which is typically used to "protect" (or react with to chemically mask) nitrogen functionality in order to lessen the toxicity of the molecule. What nucleophilic moiety in voacamine will react first with Boc anhydride?

The given molecule is known as voacamine. Multi-cyclic molecules with a high nitrogen content such as this one are known as alkaloids, and tend to be highly toxic. A chemist is attempting to react a sample of voacamine with an electrophilic reagent known as Boc anhydride, which is typically used to "protect" (or react with to chemically mask) nitrogen functionality in order to lessen the toxicity of the molecule. What nucleophilic moiety in voacamine will react first with Boc anhydride?

Tap to reveal answer
There are two major types of nitrogen-containing moieties in this molecule.
First, there are the aromatic nitrogenated groups, such as the purple, green, and gold. All three of these nitrogens, when reacted with an electrophile such as Boc anhydride, would produce positively charged species. This alone would be unfavorable, however, as these nitrogens each donate a lone pair to their aromatic systems, donating this lone pair to an electrophile would break the aromaticity of the system. Breaking aromaticity is always highly unfavorable, and hence, none of these three would readily react with Boc anhydride.
Second, there are the aliphatic nitrogenated groups, such as the red and blue. Of these two, the red is tertiary and the blue is secondary. This means the red would produce a positively charged, tetrasubstituted product when reacting with Boc anhydride, whereas the blue would not form a charged product. The blue amine is also more sterically available, and is the correct answer, as it has the best ability to act as a nucleophile.
There are two major types of nitrogen-containing moieties in this molecule.
First, there are the aromatic nitrogenated groups, such as the purple, green, and gold. All three of these nitrogens, when reacted with an electrophile such as Boc anhydride, would produce positively charged species. This alone would be unfavorable, however, as these nitrogens each donate a lone pair to their aromatic systems, donating this lone pair to an electrophile would break the aromaticity of the system. Breaking aromaticity is always highly unfavorable, and hence, none of these three would readily react with Boc anhydride.
Second, there are the aliphatic nitrogenated groups, such as the red and blue. Of these two, the red is tertiary and the blue is secondary. This means the red would produce a positively charged, tetrasubstituted product when reacting with Boc anhydride, whereas the blue would not form a charged product. The blue amine is also more sterically available, and is the correct answer, as it has the best ability to act as a nucleophile.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing nucleophilicity.

Rank the following compounds in order of increasing nucleophilicity.

Tap to reveal answer
The periodic trends of electronegativity and charge stability are useful tools for predicting nucleophilic strength. First, it is important to recognize that the two charged species,  and
and  are the two strongest nucleophiles. This is because the destabilizing negative charge present in these species may be neutralized by donating a lone pair to the formation of a chemical bond. As we know, opposite charges attract, so species bearing a full negative charge are drawn to electron-poor regions. Uncharged species such as water and ammonia carry a lone pair capable of bonding, but are less energetically drawn towards positive charges.
are the two strongest nucleophiles. This is because the destabilizing negative charge present in these species may be neutralized by donating a lone pair to the formation of a chemical bond. As we know, opposite charges attract, so species bearing a full negative charge are drawn to electron-poor regions. Uncharged species such as water and ammonia carry a lone pair capable of bonding, but are less energetically drawn towards positive charges.
Ammonia is a stronger nucleophile than water because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen. What this means is that the nitrogen-bound lone pair of ammonia is more loosely contained than the oxygen-bound lone pairs of water. As a result, they are more easily donated to form a bond at an electron-poor carbon.
From this trend, one might expect that fluoride ions would be less nucleophilic than chloride ions since fluorine is more electronegative. However, moving down a group of the periodic table, atomic radius increases. Anions are stabilized by spreading electron density across an electron cloud of greater volume, such as that of  compared to the smaller
compared to the smaller  . As such, the correct ordering of species is II, I, III, IV.
. As such, the correct ordering of species is II, I, III, IV.
The periodic trends of electronegativity and charge stability are useful tools for predicting nucleophilic strength. First, it is important to recognize that the two charged species, 

Ammonia is a stronger nucleophile than water because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen. What this means is that the nitrogen-bound lone pair of ammonia is more loosely contained than the oxygen-bound lone pairs of water. As a result, they are more easily donated to form a bond at an electron-poor carbon.
From this trend, one might expect that fluoride ions would be less nucleophilic than chloride ions since fluorine is more electronegative. However, moving down a group of the periodic table, atomic radius increases. Anions are stabilized by spreading electron density across an electron cloud of greater volume, such as that of 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is the strongest nucleophile?
Which of the following is the strongest nucleophile?
Tap to reveal answer
The molecules are almost exactly the same, except that each molecule contains a different group 6 atom. Size increases as we move down the group 6 column, and therefore nucleophelicity increases. Larger and less electronegative atoms hold onto their electrons more loosely, and are stronger nucleophiles.
The molecules are almost exactly the same, except that each molecule contains a different group 6 atom. Size increases as we move down the group 6 column, and therefore nucleophelicity increases. Larger and less electronegative atoms hold onto their electrons more loosely, and are stronger nucleophiles.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Select the strongest nucleophile in an aprotic solvent.
Select the strongest nucleophile in an aprotic solvent.
Tap to reveal answer
In aprotic solvents, nucleophilicity increases with electronegativity when dealing with atoms in the same group (column on the periodic table).
In aprotic solvents, nucleophilicity increases with electronegativity when dealing with atoms in the same group (column on the periodic table).
← Didn't Know|Knew It →