Pre-Calculus - Math
Card 1 of 228
The speed of a car traveling on the highway is given by the following function of time:

What can you say about the car's speed after a long time (that is, as  approaches infinity)?
approaches infinity)?
The speed of a car traveling on the highway is given by the following function of time:
What can you say about the car's speed after a long time (that is, as 
Tap to reveal answer
The function given is a polynomial with a term  , such that
, such that  is greater than 1.
is greater than 1.
Whenever this is the case, we can say that the whole function diverges (approaches infinity) in the limit as  approaches infinity.
approaches infinity.
This tells us that the given function is not a very realistic description of a car's speed for large  !
!
The function given is a polynomial with a term 

Whenever this is the case, we can say that the whole function diverges (approaches infinity) in the limit as 
This tells us that the given function is not a very realistic description of a car's speed for large 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Tap to reveal answer
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Calculate  .
.
Calculate 
Tap to reveal answer
This can be rewritten as follows:


![= \lim_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left [\left ( x^{2}-1 \right ) \cdot \sin \frac{1}{ x^{2}-1} \right]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/99922/gif.latex)

We can substitute  , noting that as
, noting that as  ,
,  :
:
 , which is the correct choice.
, which is the correct choice.
This can be rewritten as follows:
We can substitute 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Let  .
.
Find  .
.
Let 
Find 
Tap to reveal answer

This is a graph of  . We know that
. We know that  is undefined; therefore, there is no value for
is undefined; therefore, there is no value for  . But as we take a look at the graph, we can see that as
. But as we take a look at the graph, we can see that as  approaches 0 from the left,
approaches 0 from the left,  approaches negative infinity.
approaches negative infinity.
This can be illustrated by thinking of small negative numbers.


NOTE: Pay attention to one-sided limit specifications, as it is easy to pick the wrong answer choice if you're not careful.
 is actually infinity, not negative infinity.
is actually infinity, not negative infinity.

This is a graph of 




This can be illustrated by thinking of small negative numbers.
NOTE: Pay attention to one-sided limit specifications, as it is easy to pick the wrong answer choice if you're not careful.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Tap to reveal answer
A limit describes what  -value a function approaches as
-value a function approaches as  approaches a certain value (in this case,
approaches a certain value (in this case, 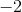 ). The easiest way to find what
). The easiest way to find what  -value a function approaches is to substitute the
-value a function approaches is to substitute the  -value into the equation.
-value into the equation.

Substituting  for
for  gives us an undefined value (which is NOT the same thing as 0). This means the function is not defined at that point. However, just because a function is undefined at a point doesn't mean it doesn't have a limit. The limit is simply whichever value the function is getting close to.
gives us an undefined value (which is NOT the same thing as 0). This means the function is not defined at that point. However, just because a function is undefined at a point doesn't mean it doesn't have a limit. The limit is simply whichever value the function is getting close to.
One method of finding the limit is to try and simplify the equation as much as possible:

As you can see, there are common factors between the numerator and the denominator that can be canceled out. (Remember, when you cancel out a factor from a rational equation, it means that the function has a hole -- an undefined point -- where that factor equals zero.)
After canceling out the common factors, we're left with:

Even though the domain of the original function is restricted ( cannot equal
cannot equal  ), we can still substitute into this simplified equation to find the limit at
), we can still substitute into this simplified equation to find the limit at 

A limit describes what 

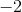


Substituting 

One method of finding the limit is to try and simplify the equation as much as possible:
As you can see, there are common factors between the numerator and the denominator that can be canceled out. (Remember, when you cancel out a factor from a rational equation, it means that the function has a hole -- an undefined point -- where that factor equals zero.)
After canceling out the common factors, we're left with:
Even though the domain of the original function is restricted (

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A function is defined by the following rational equation:

What are the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of this function's graph?
A function is defined by the following rational equation:
What are the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of this function's graph?
Tap to reveal answer
To find the horizontal asymptote, compare the degrees of the top and bottom polynomials. In this case, the two degrees are the same (1), which means that the equation of the horizontal asymptote is equal to the ratio of the leading coefficients (top : bottom). Since the numerator's leading coefficient is 1, and the denominator's leading coefficient is 2, the equation of the horizontal asymptote is  .
.
To find the vertical asymptote, set the denominator equal to zero to find when the entire function is undefined:



To find the horizontal asymptote, compare the degrees of the top and bottom polynomials. In this case, the two degrees are the same (1), which means that the equation of the horizontal asymptote is equal to the ratio of the leading coefficients (top : bottom). Since the numerator's leading coefficient is 1, and the denominator's leading coefficient is 2, the equation of the horizontal asymptote is 
To find the vertical asymptote, set the denominator equal to zero to find when the entire function is undefined:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Indicate the first three terms of the following series:

Indicate the first three terms of the following series:
Tap to reveal answer
In the arithmetic series, the first terms can be found by plugging  ,
,  , and
, and  into the equation.
into the equation.






In the arithmetic series, the first terms can be found by plugging 


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Indicate the first three terms of the following series:

Indicate the first three terms of the following series:
Tap to reveal answer
In the arithmetic series, the first terms can be found by plugging in  ,
,  , and
, and  for
for  .
.






In the arithmetic series, the first terms can be found by plugging in 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the sum of all even integers from  to
to  .
.
Find the sum of all even integers from 

Tap to reveal answer
The formula for the sum of an arithmetic series is
 ,
,
where  is the number of terms in the series,
is the number of terms in the series,  is the first term, and
is the first term, and  is the last term.
is the last term.

The formula for the sum of an arithmetic series is

where 


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the sum of all even integers from  to
to  .
.
Find the sum of all even integers from 

Tap to reveal answer
The formula for the sum of an arithmetic series is
 ,
,
where  is the number of terms in the series,
is the number of terms in the series,  is the first term, and
is the first term, and  is the last term.
is the last term.
We know that there are  terms in the series. The first term is
terms in the series. The first term is  and the last term is
and the last term is  . Our formula becomes:
. Our formula becomes:


The formula for the sum of an arithmetic series is

where 


We know that there are 


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the sum of the even integers from  to
to  .
.
Find the sum of the even integers from 

Tap to reveal answer
The sum of even integers represents an arithmetic series.
The formula for the partial sum of an arithmetic series is
 ,
,
where  is the first value in the series,
is the first value in the series,  is the number of terms, and
is the number of terms, and  is the difference between sequential terms.
is the difference between sequential terms.
Plugging in our values, we get:



The sum of even integers represents an arithmetic series.
The formula for the partial sum of an arithmetic series is

where 


Plugging in our values, we get:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the value for 
Find the value for
Tap to reveal answer
To best understand, let's write out the series. So

We can see this is an infinite geometric series with each successive term being multiplied by  .
.
A definition you may wish to remember is
 where
where  stands for the common ratio between the numbers, which in this case is
stands for the common ratio between the numbers, which in this case is  or
or  . So we get
. So we get

To best understand, let's write out the series. So
We can see this is an infinite geometric series with each successive term being multiplied by 
A definition you may wish to remember is




← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Evaluate:

Evaluate:
Tap to reveal answer
This is a geometric series whose first term is  and whose common ratio is
and whose common ratio is  . The sum of this series is:
. The sum of this series is:

This is a geometric series whose first term is 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the domain of the function below?

What is the domain of the function below?
Tap to reveal answer
The domain is defined as the set of all values of x for which the function is defined i.e. has a real result. The square root of a negative number isn't defined, so we should find the intervals where that occurs:

The square of any number is positive, so we can't eliminate any x-values yet.
If the denominator is zero, the expression will also be undefined.
Find the x-values which would make the denominator 0:

Therefore, the domain is  .
.
The domain is defined as the set of all values of x for which the function is defined i.e. has a real result. The square root of a negative number isn't defined, so we should find the intervals where that occurs:
The square of any number is positive, so we can't eliminate any x-values yet.
If the denominator is zero, the expression will also be undefined.
Find the x-values which would make the denominator 0:
Therefore, the domain is 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Evaluate:

Evaluate:
Tap to reveal answer
This is a geometric series whose first term is  and whose common ratio is
and whose common ratio is  . The sum of this series is:
. The sum of this series is:

This is a geometric series whose first term is 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Consider the sequence: 
What is the fifteenth term in the sequence?
Consider the sequence:
What is the fifteenth term in the sequence?
Tap to reveal answer
The sequence can be described by the equation  , where
, where  is the term in the sequence.
is the term in the sequence.
For the 15th term,  .
.




The sequence can be described by the equation 

For the 15th term, 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the sixth term when  is expanded?
is expanded?
What is the sixth term when 
Tap to reveal answer
We will need to use the Binomial Theorem in order to solve this problem. Consider the expansion of  , where n is an integer. The rth term of this expansion is given by the following formula:
, where n is an integer. The rth term of this expansion is given by the following formula:
 ,
,
where  is a combination. In general, if x and y are nonnegative integers such that x > y, then the combination of x and y is defined as follows:
is a combination. In general, if x and y are nonnegative integers such that x > y, then the combination of x and y is defined as follows:  .
.
We are asked to find the sixth term of  , which means that in this case r = 6 and n = 10. Also, we will let
, which means that in this case r = 6 and n = 10. Also, we will let  and
and  . We can now apply the Binomial Theorem to determine the sixth term, which is as follows:
. We can now apply the Binomial Theorem to determine the sixth term, which is as follows:


Next, let's find the value of  . According to the definition of a combination,
. According to the definition of a combination,

 .
.
Remember that, if n is a positive integer, then  . This is called a factorial.
. This is called a factorial.
Let's go back to simplifying  .
.



The answer is  .
.
We will need to use the Binomial Theorem in order to solve this problem. Consider the expansion of 

where 

We are asked to find the sixth term of 


Next, let's find the value of 

Remember that, if n is a positive integer, then 
Let's go back to simplifying 
The answer is 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What are the first three terms in the series?

What are the first three terms in the series?
Tap to reveal answer
To find the first three terms, replace  with
with  ,
,  , and
, and  .
.



The first three terms are  ,
,  , and
, and  .
.
To find the first three terms, replace 



The first three terms are 


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the first three terms in the series.

Find the first three terms in the series.
Tap to reveal answer
To find the first three terms, replace  with
with  ,
,  , and
, and  .
.



The first three terms are  ,
,  , and
, and  .
.
To find the first three terms, replace 



The first three terms are 


← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Indicate the first three terms of the following series:

Indicate the first three terms of the following series:
Tap to reveal answer
The first terms can be found by substituting  ,
,  , and
, and  for
for  into the sum formula.
into the sum formula.






The first terms can be found by substituting 



← Didn't Know|Knew It →