Quadrilaterals - Geometry
Card 1 of 600
Find the area of the rhombus shown below. You will have to find the lengths of the sides as well.

The rhombus shown has the following coordinates:

Round to the nearest hundredth.
Find the area of the rhombus shown below. You will have to find the lengths of the sides as well.

The rhombus shown has the following coordinates:
Round to the nearest hundredth.
Tap to reveal answer
Finding the area of a rhombus follows the formula:

In this rhombus, you will find that  , which are the two x coordinates.
, which are the two x coordinates.
The length of q is a more involved process. You can find q by using the Pythagorean Theorem.

 .
.
Therefore, the area is
 .
.
Finding the area of a rhombus follows the formula:
In this rhombus, you will find that 
The length of q is a more involved process. You can find q by using the Pythagorean Theorem.

Therefore, the area is

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of the rhombus below.

Find the area of the rhombus below.

Tap to reveal answer

Recall that the diagonals of the rhombus are perpendicular bisectors. From the given side and the given diagonal, we can find the length of the second diagonal by using the Pythagorean Theorem.

Let the given diagonal be diagonal 1, and rearrange the equation to solve for diagonal 2.



Plug in the given side and diagonal to find the length of diagonal 2.

Now, recall how to find the area of a rhombus:

Plug in the two diagonals to find the area.


Recall that the diagonals of the rhombus are perpendicular bisectors. From the given side and the given diagonal, we can find the length of the second diagonal by using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Let the given diagonal be diagonal 1, and rearrange the equation to solve for diagonal 2.
Plug in the given side and diagonal to find the length of diagonal 2.
Now, recall how to find the area of a rhombus:
Plug in the two diagonals to find the area.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of the rhombus below.

Find the area of the rhombus below.

Tap to reveal answer

Recall that the diagonals of the rhombus are perpendicular bisectors. From the given side and the given diagonal, we can find the length of the second diagonal by using the Pythagorean Theorem.

Let the given diagonal be diagonal 1, and rearrange the equation to solve for diagonal 2.



Plug in the given side and diagonal to find the length of diagonal 2.

Now, recall how to find the area of a rhombus:

Plug in the two diagonals to find the area.

Make sure to round to  places after the decimal.
places after the decimal.

Recall that the diagonals of the rhombus are perpendicular bisectors. From the given side and the given diagonal, we can find the length of the second diagonal by using the Pythagorean Theorem.
Let the given diagonal be diagonal 1, and rearrange the equation to solve for diagonal 2.
Plug in the given side and diagonal to find the length of diagonal 2.
Now, recall how to find the area of a rhombus:
Plug in the two diagonals to find the area.
Make sure to round to 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the area of the following kite?

What is the area of the following kite?

Tap to reveal answer
The formula for the area of a kite:
 ,
,
where  represents the length of one diagonal and
represents the length of one diagonal and  represents the length of the other diagonal.
represents the length of the other diagonal.
Plugging in our values, we get:


The formula for the area of a kite:

where 

Plugging in our values, we get:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following shapes is a kite?

Which of the following shapes is a kite?

Tap to reveal answer
A kite is a four-sided shape with straight sides that has two pairs of sides. Each pair of adjacent sides are equal in length. A square is also considered a kite.
A kite is a four-sided shape with straight sides that has two pairs of sides. Each pair of adjacent sides are equal in length. A square is also considered a kite.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Two congruent equilateral triangles with sides of length  are connected so that they share a side. Each triangle has a height of
are connected so that they share a side. Each triangle has a height of  . Express the area of the shape in terms of
. Express the area of the shape in terms of  .
.
Two congruent equilateral triangles with sides of length 


Tap to reveal answer
The shape being described is a rhombus with side lengths 1. Since they are equilateral triangles connected by one side, that side becomes the lesser diagonal, so  .
.
The greater diagonal is twice the height of the equaliteral triangles,  .
.
The area of a rhombus is half the product of the diagonals, so:

The shape being described is a rhombus with side lengths 1. Since they are equilateral triangles connected by one side, that side becomes the lesser diagonal, so 
The greater diagonal is twice the height of the equaliteral triangles, 
The area of a rhombus is half the product of the diagonals, so:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The diagonal lengths of a kite are  and
and  . What is the area?
. What is the area?
The diagonal lengths of a kite are 

Tap to reveal answer
The area of a kite is given below. Substitute the given diagonals to find the area.

The area of a kite is given below. Substitute the given diagonals to find the area.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of a kite if the length of the diagonals are  and
and  .
.
Find the area of a kite if the length of the diagonals are 

Tap to reveal answer
Substitute the given diagonals into the area formula for kites. Solve and simplify.

Substitute the given diagonals into the area formula for kites. Solve and simplify.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of a kite if the diagonal dimensions are  and
and  .
.
Find the area of a kite if the diagonal dimensions are 

Tap to reveal answer
The area of the kite is given below. The FOIL method will need to be used to simplify the binomial.


The area of the kite is given below. The FOIL method will need to be used to simplify the binomial.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of a kite if one diagonal is  long, and the other diagonal is
long, and the other diagonal is  long.
long.
Find the area of a kite if one diagonal is 

Tap to reveal answer
The formula for the area of a kite is

Plug in the values for each of the diagonals and solve.

The formula for the area of a kite is
Plug in the values for each of the diagonals and solve.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The diagonals of a kite are  and
and  . Find the area.
. Find the area.
The diagonals of a kite are 

Tap to reveal answer
The formula for the area for a kite is
 , where
, where  and
and  are the lengths of the kite's two diagonals. We are given the length of these diagonals in the problem, so we can substitute them into the formula and solve for the area:
are the lengths of the kite's two diagonals. We are given the length of these diagonals in the problem, so we can substitute them into the formula and solve for the area:

The formula for the area for a kite is



← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The diagonals of a kite are  and
and  . Express the kite's area in simplified form.
. Express the kite's area in simplified form.
The diagonals of a kite are 

Tap to reveal answer
Write the formula for the area of a kite.

Substitute the diagonals and reduce.

Multiply the parenthetical elements together by distributing the  :
:



You can consider the outermost fraction with  in the denominator as multiplying everything in the numerator by
in the denominator as multiplying everything in the numerator by  :
:


Change the added  to
to  to create a common denominator and add the fractions to arrive at the correct answer:
to create a common denominator and add the fractions to arrive at the correct answer:

Write the formula for the area of a kite.
Substitute the diagonals and reduce.
Multiply the parenthetical elements together by distributing the 
You can consider the outermost fraction with 

Change the added 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
If the diagonals of a kite are  and
and  , express the area in simplified form.
, express the area in simplified form.
If the diagonals of a kite are 

Tap to reveal answer
Write the formula for the area of a kite:

Substitute the given diagonals:

Distribute the  :
:

Create a common denominator for the two fractions in the numerator:


You can consider the outermost division by  as multiplying everything in the numerator by
as multiplying everything in the numerator by  :
:

Multiply across to arrive at the correct answer:

Write the formula for the area of a kite:
Substitute the given diagonals:
Distribute the 
Create a common denominator for the two fractions in the numerator:
You can consider the outermost division by 

Multiply across to arrive at the correct answer:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of a kite with the diagonal lengths of  and
and  .
.
Find the area of a kite with the diagonal lengths of 

Tap to reveal answer
Write the formula to find the area of a kite. Substitute the diagonals and solve.

Write the formula to find the area of a kite. Substitute the diagonals and solve.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of a kite with diagonal lengths of  and
and  .
.
Find the area of a kite with diagonal lengths of 

Tap to reveal answer
Write the formula for the area of a kite.

Plug in the given diagonals.

Pull out a common factor of two in  and simplify.
and simplify.


Use the FOIL method to simplify.


Write the formula for the area of a kite.
Plug in the given diagonals.
Pull out a common factor of two in 
Use the FOIL method to simplify.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Show algebraically how the formula of the area of a kite is developed.

Show algebraically how the formula of the area of a kite is developed.

Tap to reveal answer
-
The given kite is divded into two congruent triangles.
-
Each triangle has a height  and a base
and a base  .
.
-
The area  of each triangle is
of each triangle is  .
.
-
The areas of the two triangles are added together,




-
The given kite is divded into two congruent triangles.
-
Each triangle has a height
and a base
.
-
The area
of each triangle is
.
-
The areas of the two triangles are added together,
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Find the area of a kite, if the diagonals of the kite are  .
.
Find the area of a kite, if the diagonals of the kite are 
Tap to reveal answer
You find the area of a kite by using the lengths of the diagonals.

 , which is equal to
, which is equal to  .
.
You can reduce this to,
 for the final answer.
for the final answer.
You find the area of a kite by using the lengths of the diagonals.


You can reduce this to,

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The rectangle area  is 220. What is the area
is 220. What is the area  of the inscribed
of the inscribed
kite  ?
?

The rectangle area 

kite 

Tap to reveal answer
-
The measures of the kite diagonals  and
and  have to be found.
have to be found.
-
Using the circumscribed rectangle,  , and
, and  .
.
-
 has to be found to find
has to be found to find  .
.
-
The rectangle area  .
.
-
 .
.
-
From step 1) and step 2), using substitution,  .
.
-
Solving the equation for x,




-

-
Kite area 
-
The measures of the kite diagonals
and
have to be found.
-
Using the circumscribed rectangle,
, and
.
-
has to be found to find
.
-
The rectangle area
.
-
.
-
From step 1) and step 2), using substitution,
.
-
Solving the equation for x,
-
-
Kite area
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
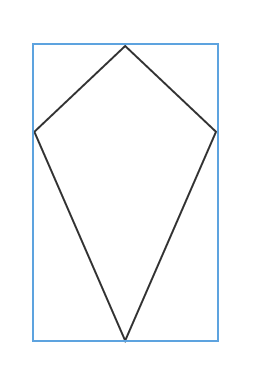
The area of the rectangle is  , what is the area of the kite?
, what is the area of the kite?

The area of the rectangle is 
Tap to reveal answer
The area of a kite is half the product of the diagonals.

The diagonals of the kite are the height and width of the rectangle it is superimposed in, and we know that because the area of a rectangle is base times height.
Therefore our equation becomes:
 .
.
We also know the area of the rectangle is  . Substituting this value in we get the following:
. Substituting this value in we get the following:

Thus,, the area of the kite is  .
.
The area of a kite is half the product of the diagonals.
The diagonals of the kite are the height and width of the rectangle it is superimposed in, and we know that because the area of a rectangle is base times height.
Therefore our equation becomes:

We also know the area of the rectangle is 
Thus,, the area of the kite is 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Given: Quadrilateral  such that
such that  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  is a right angle, and diagonal
is a right angle, and diagonal  has length 24.
has length 24.
Give the length of diagonal  .
.
Given: Quadrilateral 





Give the length of diagonal 
Tap to reveal answer
The Quadrilateral  is shown below with its diagonals
is shown below with its diagonals  and
and  .
.
. We call the point of intersection  :
:

The diagonals of a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent congruent sides - a kite - are perpendicular; also,  bisects the
bisects the  and
and  angles of the kite. Consequently,
angles of the kite. Consequently,  is a 30-60-90 triangle and
is a 30-60-90 triangle and  is a 45-45-90 triangle. Also, the diagonal that connects the common vertices of the pairs of adjacent sides bisects the other diagonal, making
is a 45-45-90 triangle. Also, the diagonal that connects the common vertices of the pairs of adjacent sides bisects the other diagonal, making  the midpoint of
the midpoint of  . Therefore,
. Therefore,
 .
.
By the 30-60-90 Theorem, since  and
and  are the short and long legs of
are the short and long legs of  ,
,

By the 45-45-90 Theorem, since  and
and  are the legs of a 45-45-90 Theorem,
are the legs of a 45-45-90 Theorem,
 .
.
The diagonal  has length
has length
 .
.
The Quadrilateral 


. We call the point of intersection 

The diagonals of a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent congruent sides - a kite - are perpendicular; also, 







By the 30-60-90 Theorem, since 


By the 45-45-90 Theorem, since 


The diagonal 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →