Patterns of Light and Stars - 5th Grade Science
Card 1 of 160
A series of photographs of a 1-meter stick and shadow were taken throughout the day. Students analyzed the photos and recorded the data in the table below. What pattern(s) are revealed about the length of the shadow in the provided data?

A series of photographs of a 1-meter stick and shadow were taken throughout the day. Students analyzed the photos and recorded the data in the table below. What pattern(s) are revealed about the length of the shadow in the provided data?

Tap to reveal answer
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. In this investigation, a series of time-lapsed photos were taken from 6:00 am until 8:00 pm, and students measured the length of the shadow that a 1-meter long stick created as well as the angle of the shadow. When reviewing the data, a pattern was revealed about the length of the shadow. The length of the shadow decreased throughout the day until it reached its shortest measurement at the Sun's peak. The length of the shadows increased after this peak. Looking at the column labeled "length," the measurements are increasing until the Sun reaches its peak during the 1:00 pm hour. After the Sun is no longer at its highest point, the length of the shadow begins to increase again. The angle of the shadows also decreased throughout the day. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made.
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. In this investigation, a series of time-lapsed photos were taken from 6:00 am until 8:00 pm, and students measured the length of the shadow that a 1-meter long stick created as well as the angle of the shadow. When reviewing the data, a pattern was revealed about the length of the shadow. The length of the shadow decreased throughout the day until it reached its shortest measurement at the Sun's peak. The length of the shadows increased after this peak. Looking at the column labeled "length," the measurements are increasing until the Sun reaches its peak during the 1:00 pm hour. After the Sun is no longer at its highest point, the length of the shadow begins to increase again. The angle of the shadows also decreased throughout the day. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Mrs. Sweeterman's class is investigating shadows today in the science lab. She hands out a task card, a sheet of large white paper, a cup, and a flashlight to each group. They take turns holding the flashlight in various positions to observe the shadow made by the cup on paper. When all of the students finished their observations, the class discussed the shadows they made and how the amount of light impacted the size of the shadows. Their observations are documented below.

What caused the shadow to change during the investigation?
Mrs. Sweeterman's class is investigating shadows today in the science lab. She hands out a task card, a sheet of large white paper, a cup, and a flashlight to each group. They take turns holding the flashlight in various positions to observe the shadow made by the cup on paper. When all of the students finished their observations, the class discussed the shadows they made and how the amount of light impacted the size of the shadows. Their observations are documented below.

What caused the shadow to change during the investigation?
Tap to reveal answer
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made. Based on the investigation that Mrs. Sweeterman's class conducted, it can be concluded that there is a relationship between the position of the cup and the position, length, and angle of the shadow. As the cup (Earth) moved positions, the shadow changed as well. The angle and length of the shadow also vary when the position of the cup (Earth) changes.
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made. Based on the investigation that Mrs. Sweeterman's class conducted, it can be concluded that there is a relationship between the position of the cup and the position, length, and angle of the shadow. As the cup (Earth) moved positions, the shadow changed as well. The angle and length of the shadow also vary when the position of the cup (Earth) changes.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A series of photographs of a 1-meter stick and shadow were taken throughout the day. Students analyzed the photos and recorded the data in the table below. What pattern(s) are revealed about the angle of the shadow in the provided data?

A series of photographs of a 1-meter stick and shadow were taken throughout the day. Students analyzed the photos and recorded the data in the table below. What pattern(s) are revealed about the angle of the shadow in the provided data?

Tap to reveal answer
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. In this investigation, a series of time-lapsed photos were taken from 6:00 am until 8:00 pm, and students measured the length of the shadow that a 1-meter long stick created as well as the angle of the shadow. When reviewing the data, a pattern was revealed about the angles of the shadow. The angle of the shadow decreased throughout the day until sunset when the shadow disappeared. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made. A prediction could be made that a similar measurement of angles would be found tomorrow and each day thereafter.
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. In this investigation, a series of time-lapsed photos were taken from 6:00 am until 8:00 pm, and students measured the length of the shadow that a 1-meter long stick created as well as the angle of the shadow. When reviewing the data, a pattern was revealed about the angles of the shadow. The angle of the shadow decreased throughout the day until sunset when the shadow disappeared. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made. A prediction could be made that a similar measurement of angles would be found tomorrow and each day thereafter.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A series of photographs of a 1-meter stick and shadow were taken throughout the day. Students analyzed the photos and recorded the data in the table below. Based on this data, what can be predicted to happen with the shadows tomorrow if measured at the same time?

A series of photographs of a 1-meter stick and shadow were taken throughout the day. Students analyzed the photos and recorded the data in the table below. Based on this data, what can be predicted to happen with the shadows tomorrow if measured at the same time?

Tap to reveal answer
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. In this investigation, a series of time-lapsed photos were taken from 6:00 am until 8:00 pm, and students measured the length of the shadow that a 1-meter long stick created as well as the angle of the shadow. When reviewing the data, a pattern was revealed about the length of the shadow. The length of the shadow decreased throughout the day until it reached its shortest measurement at the Sun's peak. The length of the shadows increased after this peak. Looking at the column labeled "length," the measurements are increasing until the Sun reaches its peak during the 1:00 pm hour. After the Sun is no longer at its highest point, the length of the shadow begins to increase again. The angles decrease as the day progresses until nighttime begins, and there is no shadow. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made. The trend will be the same tomorrow to the measurements will be very similar. There might be a slight difference because the Earth has traveled another day in its revolution around the Sun.
Data tables are a great way to organize and analyze information from an investigation or experiment. In this investigation, a series of time-lapsed photos were taken from 6:00 am until 8:00 pm, and students measured the length of the shadow that a 1-meter long stick created as well as the angle of the shadow. When reviewing the data, a pattern was revealed about the length of the shadow. The length of the shadow decreased throughout the day until it reached its shortest measurement at the Sun's peak. The length of the shadows increased after this peak. Looking at the column labeled "length," the measurements are increasing until the Sun reaches its peak during the 1:00 pm hour. After the Sun is no longer at its highest point, the length of the shadow begins to increase again. The angles decrease as the day progresses until nighttime begins, and there is no shadow. Analyzing data can often lead to patterns being recognized, and predictions about future measurements can be made. The trend will be the same tomorrow to the measurements will be very similar. There might be a slight difference because the Earth has traveled another day in its revolution around the Sun.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The orbits of Earth around the Sun and of the Moon around Earth, together with the rotation of Earth about an axis between its north and south poles, cause observable patterns. These include daily changes in the length and direction of shadows.
The orbits of Earth around the Sun and of the Moon around Earth, together with the rotation of Earth about an axis between its north and south poles, cause observable patterns. These include daily changes in the length and direction of shadows.
Tap to reveal answer
The statement in the question is correct. Patterns within shadows can be seen by measuring the length and direction and comparing them daily. The Earth's rotation causes the shadows to change throughout the day. The rotation of the Earth also causes day and night. The Earth's revolution causes slight changes in the length of these things because of its location in orbit.
The statement in the question is correct. Patterns within shadows can be seen by measuring the length and direction and comparing them daily. The Earth's rotation causes the shadows to change throughout the day. The rotation of the Earth also causes day and night. The Earth's revolution causes slight changes in the length of these things because of its location in orbit.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The NASA provided photo below is depicting what shadow pattern that happens nightly?

The NASA provided photo below is depicting what shadow pattern that happens nightly?

Tap to reveal answer
The shadow pattern that is depicted in the photo is the moon phases. The picture demonstrates where the Moon is located in regard to the Earth and how the Moon appears to us.
NASA explains more about this cycle, "If you have looked into the night sky, you may have noticed the Moon appears to change shape each night. Some nights, the Moon might look like a narrow crescent. Other nights, the Moon might look like a bright circle. And on other nights, you might not be able to see the Moon at all. The different shapes of the Moon that we see at different times of the month are called the Moon’s phases. The Moon does not produce its own light. There is only one source of light in our solar system, and that is the Sun. Without the Sun, our Moon would be completely dark. What you may have heard referred to as “moonlight” is actually just sunlight reflecting off of the Moon’s surface. The Sun’s light comes from one direction, and it always illuminates, or lights up, one half of the Moon – the side of the Moon that is facing the Sun. The other side of the Moon is dark."
The shadow pattern that is depicted in the photo is the moon phases. The picture demonstrates where the Moon is located in regard to the Earth and how the Moon appears to us.
NASA explains more about this cycle, "If you have looked into the night sky, you may have noticed the Moon appears to change shape each night. Some nights, the Moon might look like a narrow crescent. Other nights, the Moon might look like a bright circle. And on other nights, you might not be able to see the Moon at all. The different shapes of the Moon that we see at different times of the month are called the Moon’s phases. The Moon does not produce its own light. There is only one source of light in our solar system, and that is the Sun. Without the Sun, our Moon would be completely dark. What you may have heard referred to as “moonlight” is actually just sunlight reflecting off of the Moon’s surface. The Sun’s light comes from one direction, and it always illuminates, or lights up, one half of the Moon – the side of the Moon that is facing the Sun. The other side of the Moon is dark."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A moon phase is one of the shapes the moon seems to have as it orbits Earth. When Earth is between the moon and the sun, you see a Full Moon. When the moon is between Earth and the sun, you can’t see the moon at all. What is this phase called?
A moon phase is one of the shapes the moon seems to have as it orbits Earth. When Earth is between the moon and the sun, you see a Full Moon. When the moon is between Earth and the sun, you can’t see the moon at all. What is this phase called?
Tap to reveal answer
The shadow pattern that is depicted in the photo is the moon phases. The picture demonstrates where the Moon is located in regard to the Earth and how the Moon appears to us.
NASA explains more about this cycle, “If you have looked into the night sky, you may have noticed the Moon appears to change shape each night. Some nights, the Moon might look like a narrow crescent. Other nights, the Moon might look like a bright circle. And on other nights, you might not be able to see the Moon at all. The different shapes of the Moon that we see at different times of the month are called the Moon’s phases. The Moon does not produce its own light. There is only one source of light in our solar system, and that is the Sun. Without the Sun, our Moon would be completely dark. What you may have heard referred to as “moonlight” is actually just sunlight reflecting off of the Moon’s surface. The Sun’s light comes from one direction, and it always illuminates, or lights up, one half of the Moon – the side of the Moon that is facing the Sun. The other side of the Moon is dark.”
The shadow pattern that is depicted in the photo is the moon phases. The picture demonstrates where the Moon is located in regard to the Earth and how the Moon appears to us.
NASA explains more about this cycle, “If you have looked into the night sky, you may have noticed the Moon appears to change shape each night. Some nights, the Moon might look like a narrow crescent. Other nights, the Moon might look like a bright circle. And on other nights, you might not be able to see the Moon at all. The different shapes of the Moon that we see at different times of the month are called the Moon’s phases. The Moon does not produce its own light. There is only one source of light in our solar system, and that is the Sun. Without the Sun, our Moon would be completely dark. What you may have heard referred to as “moonlight” is actually just sunlight reflecting off of the Moon’s surface. The Sun’s light comes from one direction, and it always illuminates, or lights up, one half of the Moon – the side of the Moon that is facing the Sun. The other side of the Moon is dark.”
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Antwon researched the lengths of day and night in different parts of the world on the same day. He created a data table to display the number of daylight hours a specific latitude received on the same day (November 8th). What pattern(s) does the data table reveal about the length of day and night?

Antwon researched the lengths of day and night in different parts of the world on the same day. He created a data table to display the number of daylight hours a specific latitude received on the same day (November 8th). What pattern(s) does the data table reveal about the length of day and night?

Tap to reveal answer
Antwon using a data table to present the information is a clear and organized way to help others understand what his research revealed. Based on the data, it can be seen that as the number of daylight hours increases, the number of nighttime hours decreases the further south traveled. At a latitude of 90o South, there are 24 hours of sunlight and 0 minutes/hours of daylight compared to a latitude of 90o North where there is absolutely no daylight. Analyzing data can reveal patterns that help us understand the natural world and make predictions about future events.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this change takes place, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
Antwon using a data table to present the information is a clear and organized way to help others understand what his research revealed. Based on the data, it can be seen that as the number of daylight hours increases, the number of nighttime hours decreases the further south traveled. At a latitude of 90o South, there are 24 hours of sunlight and 0 minutes/hours of daylight compared to a latitude of 90o North where there is absolutely no daylight. Analyzing data can reveal patterns that help us understand the natural world and make predictions about future events.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this change takes place, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
An Earth day is 24 hours because the Earth spins on its axis once every 24 hours.
An Earth day is 24 hours because the Earth spins on its axis once every 24 hours.
Tap to reveal answer
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The Earth rotating on its axis is the cause for day and night. When it is daytime for half of Earth, it is nighttime for the other half.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The Earth rotating on its axis is the cause for day and night. When it is daytime for half of Earth, it is nighttime for the other half.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Why is half of the Earth dark and the other half white in this diagram?
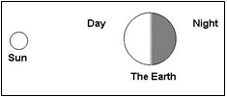
Source of diagram: The Victoria State Education and Training department
Why is half of the Earth dark and the other half white in this diagram?

Source of diagram: The Victoria State Education and Training department
Tap to reveal answer
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why half of the Earth is in nighttime and the other daytime, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
At any one time, half of the Earth's sphere is in sunlight while the other half is in darkness. The Earth's rotation causes this change to take place every day. It is a predictable pattern that we can count on.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why half of the Earth is in nighttime and the other daytime, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
At any one time, half of the Earth's sphere is in sunlight while the other half is in darkness. The Earth's rotation causes this change to take place every day. It is a predictable pattern that we can count on.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Mr. Green's class is studying the Solar System and Milky Way Galaxy. Today they are doing an investigation in the lab. Asia and Chele are partners for today's activity. They are given a ping pong ball with a sticker on one side, a flashlight, and their lab journals with a pencil for recording observations or data. Mr. Green turns off the lights. Asia holds the ping pong ball that represents Earth at a slight angle (like its axis) while Chele shines a flashlight on the center of the ball. Asia slowly rotates the Earth counterclockwise, and they observe where the light shines and where it doesn't. They take notice of the sticker and whether the sun shines on it or it is in darkness while the Earth rotates. Their observations are below.

Based on Asia and Chele's observations, how do we know which areas of the world are experiencing daytime?
Mr. Green's class is studying the Solar System and Milky Way Galaxy. Today they are doing an investigation in the lab. Asia and Chele are partners for today's activity. They are given a ping pong ball with a sticker on one side, a flashlight, and their lab journals with a pencil for recording observations or data. Mr. Green turns off the lights. Asia holds the ping pong ball that represents Earth at a slight angle (like its axis) while Chele shines a flashlight on the center of the ball. Asia slowly rotates the Earth counterclockwise, and they observe where the light shines and where it doesn't. They take notice of the sticker and whether the sun shines on it or it is in darkness while the Earth rotates. Their observations are below.

Based on Asia and Chele's observations, how do we know which areas of the world are experiencing daytime?
Tap to reveal answer
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Mr. Green's class is studying the Solar System and Milky Way Galaxy. Today they are doing an investigation in the lab. Asia and Chele are partners for today's activity. They are given a ping pong ball with a sticker on one side, a flashlight, and their lab journals with a pencil for recording observations or data. Mr. Green turns off the lights. Asia holds the ping pong ball that represents Earth at a slight angle (like its axis) while Chele shines a flashlight on the center of the ball. Asia slowly rotates the Earth counterclockwise, and they observe where the light shines and where it doesn't. They take notice of the sticker and whether the sun shines on it or it is in darkness while the Earth rotates. Their observations are below.

How does the amount of sunlight change as the Earth rotates?
Mr. Green's class is studying the Solar System and Milky Way Galaxy. Today they are doing an investigation in the lab. Asia and Chele are partners for today's activity. They are given a ping pong ball with a sticker on one side, a flashlight, and their lab journals with a pencil for recording observations or data. Mr. Green turns off the lights. Asia holds the ping pong ball that represents Earth at a slight angle (like its axis) while Chele shines a flashlight on the center of the ball. Asia slowly rotates the Earth counterclockwise, and they observe where the light shines and where it doesn't. They take notice of the sticker and whether the sun shines on it or it is in darkness while the Earth rotates. Their observations are below.

How does the amount of sunlight change as the Earth rotates?
Tap to reveal answer
The amount of sunlight changes at a location based on whether they are facing towards the Sun or away from the Sun. When facing directly towards the Sun, an area will experience daytime while the opposite side of Earth experiences night. The light starts to dim as the Earth rotates, and the location begins to experience nighttime. As the rotation takes place, the opposite of Earth becomes lighter as daytime begins.
The amount of sunlight changes at a location based on whether they are facing towards the Sun or away from the Sun. When facing directly towards the Sun, an area will experience daytime while the opposite side of Earth experiences night. The light starts to dim as the Earth rotates, and the location begins to experience nighttime. As the rotation takes place, the opposite of Earth becomes lighter as daytime begins.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Why do the Sun and the Moon appear to move across the sky from east to west instead of remaining in one place?
Why do the Sun and the Moon appear to move across the sky from east to west instead of remaining in one place?
Tap to reveal answer
The amount of sunlight changes at a location based on whether they are facing towards the Sun or away from the Sun. When facing directly towards the Sun, an area will experience daytime while the opposite side of Earth experiences night. The light starts to dim as the Earth rotates, and the location begins to experience nighttime. As the rotation takes place, the opposite of Earth becomes lighter as daytime begins.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The amount of sunlight changes at a location based on whether they are facing towards the Sun or away from the Sun. When facing directly towards the Sun, an area will experience daytime while the opposite side of Earth experiences night. The light starts to dim as the Earth rotates, and the location begins to experience nighttime. As the rotation takes place, the opposite of Earth becomes lighter as daytime begins.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of these is a direct result of Earth's rotation?
Which of these is a direct result of Earth's rotation?
Tap to reveal answer
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun. This rotation leads to a 24 hour day on Earth.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun. This rotation leads to a 24 hour day on Earth.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Why does Earth have day and night?
Why does Earth have day and night?
Tap to reveal answer
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following motions defines the length of Earth's day?
Which of the following motions defines the length of Earth's day?
Tap to reveal answer
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Jimena knows that Earth rotates on its axis. How much time has passed after one rotation of Earth on its axis?
Jimena knows that Earth rotates on its axis. How much time has passed after one rotation of Earth on its axis?
Tap to reveal answer
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
If you were to watch the night sky from dusk to dawn, you would notice starts rising from the eastern horizon. They will sweep across the night sky and set beneath the western horizon at dawn. Something interesting happens over time. If you were to look outside again a few weeks later, those same stars would disappear from your view. A new group of stars would take their place. In the winter months, stargazers in the Northern Hemisphere look into the night sky and see Orion the Hunter. The same spot in the summertime revels the stars of Scorpius. In the spring, the constellation of the Sickle of Leo, the Lion, is present. Finally, in the fall, the Great Square of Pegasus comes into view. Every season this same pattern takes place, and the constellations return to the skywatcher's view.
As our Earth whirls through space around the Sun, its motions cause night and day, the four seasons, and the passage of the years. The Earth completes a single turn on its axis, not in 24 hours, but 23 hours 56 minutes. As a result, the stars appear to rise, cross the sky and set four minutes earlier each night. The Earth does not merely stand in the same spot in space and spins but is always rushing eastward along in its orbit around the Sun.
What patterns in the stars do we notice when observing the night sky?
If you were to watch the night sky from dusk to dawn, you would notice starts rising from the eastern horizon. They will sweep across the night sky and set beneath the western horizon at dawn. Something interesting happens over time. If you were to look outside again a few weeks later, those same stars would disappear from your view. A new group of stars would take their place. In the winter months, stargazers in the Northern Hemisphere look into the night sky and see Orion the Hunter. The same spot in the summertime revels the stars of Scorpius. In the spring, the constellation of the Sickle of Leo, the Lion, is present. Finally, in the fall, the Great Square of Pegasus comes into view. Every season this same pattern takes place, and the constellations return to the skywatcher's view.
As our Earth whirls through space around the Sun, its motions cause night and day, the four seasons, and the passage of the years. The Earth completes a single turn on its axis, not in 24 hours, but 23 hours 56 minutes. As a result, the stars appear to rise, cross the sky and set four minutes earlier each night. The Earth does not merely stand in the same spot in space and spins but is always rushing eastward along in its orbit around the Sun.
What patterns in the stars do we notice when observing the night sky?
Tap to reveal answer
The patterns of stars in the sky stay the same, although they appear to move across the sky nightly. In a single location, the same stars or constellations are not seen nightly but instead seasonally. As the Earth revolves around the Sun, a variety of stars are visible because of the Earth's location in its orbit.
The patterns of stars in the sky stay the same, although they appear to move across the sky nightly. In a single location, the same stars or constellations are not seen nightly but instead seasonally. As the Earth revolves around the Sun, a variety of stars are visible because of the Earth's location in its orbit.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
If you were to watch the night sky from dusk to dawn, you would notice starts rising from the eastern horizon. They will sweep across the night sky and set beneath the western horizon at dawn. Something interesting happens over time. If you were to look outside again a few weeks later, those same stars would disappear from your view. A new group of stars would take their place. In the winter months, stargazers in the Northern Hemisphere look into the night sky and see Orion the Hunter. The same spot in the summertime revels the stars of Scorpius. In the spring, the constellation of the Sickle of Leo, the Lion, is present. Finally, in the fall, the Great Square of Pegasus comes into view. Every season this same pattern takes place, and the constellations return to the skywatcher's view.
As our Earth whirls through space around the Sun, its motions cause night and day, the four seasons, and the passage of the years. The Earth completes a single turn on its axis, not in 24 hours, but 23 hours 56 minutes. As a result, the stars appear to rise, cross the sky and set four minutes earlier each night. The Earth does not merely stand in the same spot in space and spins but is always rushing eastward along in its orbit around the Sun.
Based on this information, which constellation(s) will be visible next summer in the Northern Hemisphere?
If you were to watch the night sky from dusk to dawn, you would notice starts rising from the eastern horizon. They will sweep across the night sky and set beneath the western horizon at dawn. Something interesting happens over time. If you were to look outside again a few weeks later, those same stars would disappear from your view. A new group of stars would take their place. In the winter months, stargazers in the Northern Hemisphere look into the night sky and see Orion the Hunter. The same spot in the summertime revels the stars of Scorpius. In the spring, the constellation of the Sickle of Leo, the Lion, is present. Finally, in the fall, the Great Square of Pegasus comes into view. Every season this same pattern takes place, and the constellations return to the skywatcher's view.
As our Earth whirls through space around the Sun, its motions cause night and day, the four seasons, and the passage of the years. The Earth completes a single turn on its axis, not in 24 hours, but 23 hours 56 minutes. As a result, the stars appear to rise, cross the sky and set four minutes earlier each night. The Earth does not merely stand in the same spot in space and spins but is always rushing eastward along in its orbit around the Sun.
Based on this information, which constellation(s) will be visible next summer in the Northern Hemisphere?
Tap to reveal answer
The Earth completes its orbit around the Sun or its revolution in about 365 days total. As the Earth revolves around the Sun, the position of the Earth changes, and this creates the different views of the night sky. Day and night are caused by the Earth's rotation or spin on its axis. This rotation is what causes daylight and nighttime. As the Earth changes its position, the stars appear to move in the sky as well. The stars are stationary but seem to move in the sky. Each day the Earth travels further in its orbit, and a different part of the night sky is visible. The stars appear seasonally, so the pattern will remain the same. Scorpius will appear each summer in the Northern Hemisphere following this pattern.
The Earth completes its orbit around the Sun or its revolution in about 365 days total. As the Earth revolves around the Sun, the position of the Earth changes, and this creates the different views of the night sky. Day and night are caused by the Earth's rotation or spin on its axis. This rotation is what causes daylight and nighttime. As the Earth changes its position, the stars appear to move in the sky as well. The stars are stationary but seem to move in the sky. Each day the Earth travels further in its orbit, and a different part of the night sky is visible. The stars appear seasonally, so the pattern will remain the same. Scorpius will appear each summer in the Northern Hemisphere following this pattern.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Some stars and constellations can be seen in the sky all year, while others appear only at certain times of the year.
Some stars and constellations can be seen in the sky all year, while others appear only at certain times of the year.
Tap to reveal answer
The Earth completes its orbit around the Sun or its revolution in about 365 days total. As the Earth revolves around the Sun, the position of the Earth changes, and this creates the different views of the night sky. Day and night are caused by the Earth's rotation or spin on its axis. This rotation is what causes daylight and nighttime. As the Earth changes its position, the stars appear to move in the sky as well. The stars are stationary but seem to move in the sky. Each day the Earth travels further in its orbit, and a different part of the night sky is visible. The stars appear seasonally, so the pattern will remain the same. The same stars will appear each summer in the Northern Hemisphere following this pattern, as will those in the other seasons.
The Earth completes its orbit around the Sun or its revolution in about 365 days total. As the Earth revolves around the Sun, the position of the Earth changes, and this creates the different views of the night sky. Day and night are caused by the Earth's rotation or spin on its axis. This rotation is what causes daylight and nighttime. As the Earth changes its position, the stars appear to move in the sky as well. The stars are stationary but seem to move in the sky. Each day the Earth travels further in its orbit, and a different part of the night sky is visible. The stars appear seasonally, so the pattern will remain the same. The same stars will appear each summer in the Northern Hemisphere following this pattern, as will those in the other seasons.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →